Regarding printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, four key stages must be considered when purchasing PCB equipment: paste application, automated component placement, soldering, and inspection.
Each stage requires different equipment to ensure the PCB is built correctly, will function as intended, and be up to standards. In this article, we’ll go through each of the four stages, the commonly used equipment, and what should be used on your PCP equipment list.
First Stage
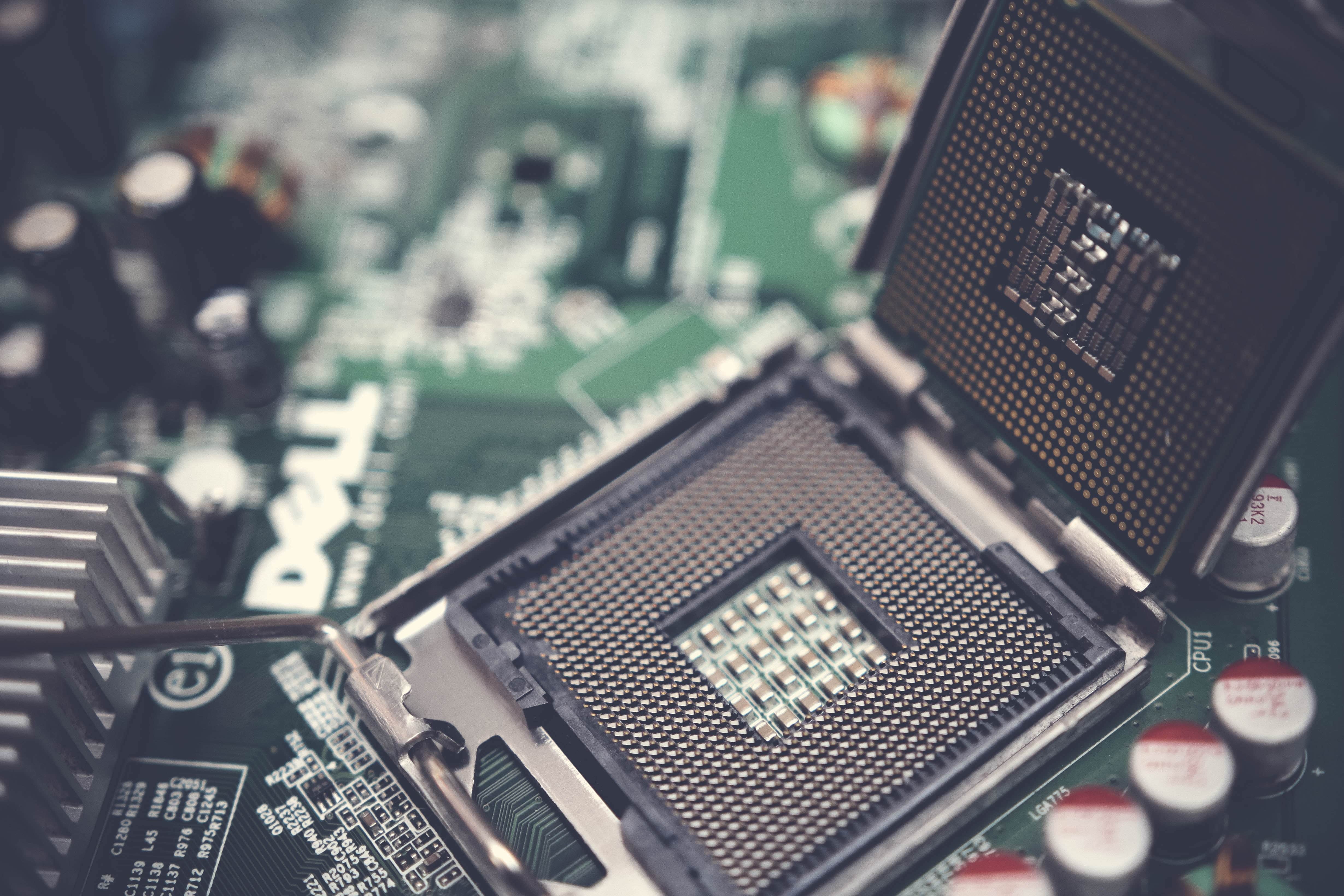
Assembling a PCB involves placing various electronic components on a printed circuit board. During this process, paste application is used to apply a small amount of solder paste to the pads on the PCB before the components are placed on them.
The paste application method involves using a stencil to apply the paste onto the board’s surface. The stencil is typically made of a thin metal sheet with cutouts or holes in the shape of the component pads.
Solder Paste Printing Machine
A solder paste printing machine is a specialized PCB equipment used in electronics manufacturing to deposit solder paste onto printed circuit boards before placing surface mount technology (SMT) components.
This process is essential in producing high-quality electronic devices, ensuring reliability and consistency in the final product.
Solder Paste Inspection (Spi) Machine
A Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) machine is a type of automated inspection system used in electronics manufacturing to inspect the accuracy and quality of solder paste deposits on printed circuit boards.
The machine uses a high-resolution camera and advanced software that analyzes the images to verify the solder paste deposits’ quantity, positioning, and alignment. SPI machines help ensure the PCBs are correctly assembled, minimizing defects, reducing rework, and improving yield.
Second Stage
Automated component placement in PCB assembly refers to using machines or robots to accurately position and mount surface-mount components on a printed circuit board.
These pieces of PCB equipment use vision systems and advanced algorithms to identify each component’s location and orientation, pick it up from a feeding system, and precisely place it onto the PCB.
This technique improves the assembly process’s speed, accuracy, and reliability, reduces the need for manual labor, and increases the overall quality of the finished product.
Glue Dispensing Machine
The glue dispensing machine in PCB assembly is a robotic dispenser used to apply adhesive compounds to printed circuit boards during assembly. This helps ensure that the components are securely bonded to the board and prevents movement or displacement during the subsequent manufacturing processes.
Pick-And-Place Machine
A pick-and-place machine is a component of the PCB assembly process that places surface-mount devices (SMD) on a printed circuit board. SMDs are small electronic components such as capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits that can be mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB.
Pick-And-Place machines can set up to 30,000 components an hour. The pick-and-place machine automates the process of picking up these small components. This is a fast and efficient way of placing many SMD components onto a PCB board, making the assembly process faster, more accurate, and cost-effective.
Third Stage
Soldering in PCB assembly refers to joining electronic components and circuit parts to a printed circuit board by melting and fusing a metal alloy with a low melting point called solder.
Some other steps before the products are complete will involve adhesives or bindings. Part of that is ensuring that a proper flex adhesive is chosen so that the layers of the board will stay together.
Black FR4 is an epoxy-based laminate material used to assemble printed circuit boards. It is a widely used substrate material for PCBs, particularly for high-performance applications that require excellent electrical and mechanical properties.
Reflow Soldering machine
Reflow soldering machine is used in the printed circuit board assembly process. It attaches surface mount components to the PCB by melting the solder paste applied to the pads on the board.
The reflow soldering process involves heating the board to a specific temperature for a particular time to melt the solder paste and create a strong bond between the component leads and the PCB pads.
Boards made with polyimide (sometimes referred to as flex core) are often put through the reflow soldering process because of their high durability.
Wave Soldering Machine
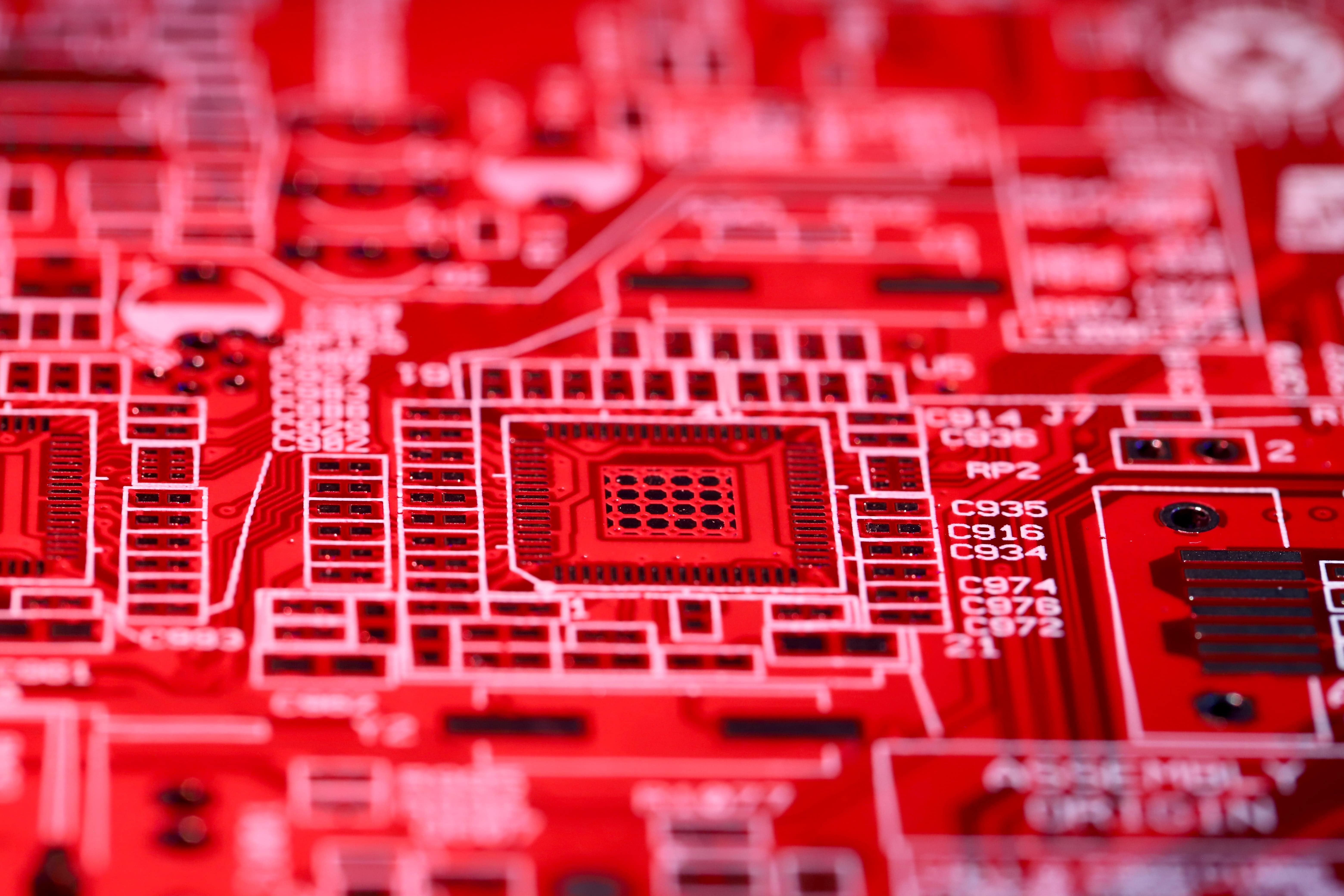
It works by passing the PCB over a bath of molten solder, maintained at a precise temperature, and then passing it through a wave of solder created by a pump.
The PCB is typically prepped by applying a flux layer to the areas where components will be placed. The flux helps clean the surface and promotes better solder adhesion.
As the PCB passes through the wave of solder, the solder adheres to the exposed metal surfaces of the electronic components and the PCB itself, creating a permanent electrical connection. The wave soldering process is especially effective for through-hole components with leads that extend through the PCB.
Fourth Stage
Inspection is a critical step in the PCB assembly process that involves examining the assembled board to ensure that it meets the required quality standards. The inspection process helps to identify defects, errors, or other issues that could impact the functionality or reliability of the board.
Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) Machine
An Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) machine is used in the printed circuit board assembly process to inspect PCBs for defects and errors. It uses a combination of cameras, lighting, and image recognition software to perform a non-contact visual inspection of the PCBs.
In-Circuit Test (ICT) Fixture
An In-Circuit Test (ICT) fixture is specialized PCB equipment used in the printed circuit board assembly process to test the electrical functionality of a PCB. The ICT fixture is designed to hold the PCB in place and contact various test points on the board to perform a series of tests.
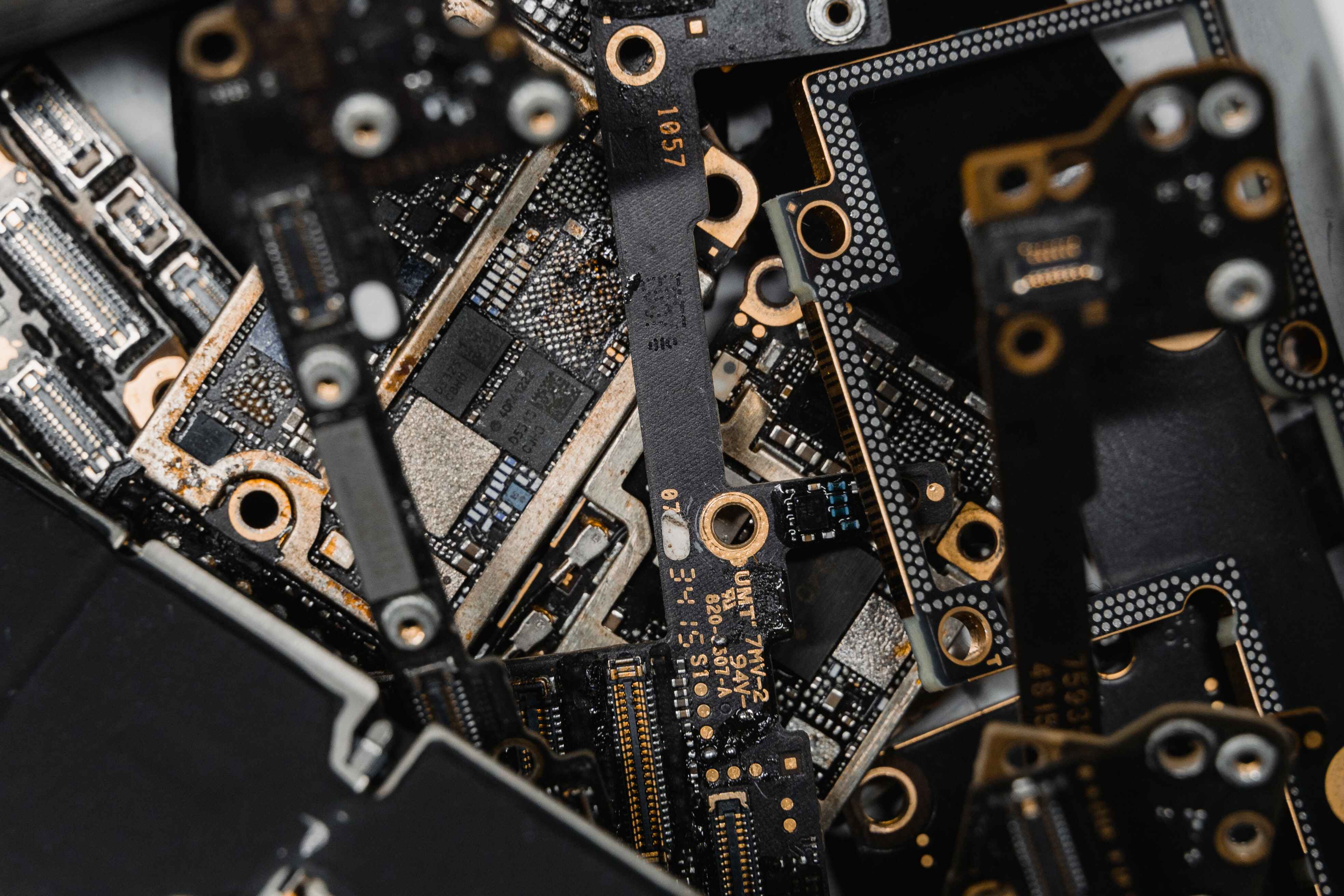
Electrical tests are performed on the PCB during the ICT process, including measuring resistance, capacitance, and voltage levels. The test results are compared to a reference value to detect any discrepancies or defects in the PCB.
Functional Validation Test (Fvt) Fixture
The Functional Validation Test (FVT) fixture is PCB equipment used in the printed circuit board assembly process to test the functionality of the PCB. The FVT fixture is designed to simulate the end-use environment of the PCB and to test its performance under various conditions.
The FVT fixture typically includes a series of sensors, actuators, and other components that can simulate the various inputs and outputs of the PCB.


